Calculating Carbon Credits for Renewable Energy
This guide outlines the process for calculating carbon credits from renewable energy projects, focusing on key standards and a simplified methodology. It includes a case study for a 1 MW solar power plant producing 8,000 MWh annually.
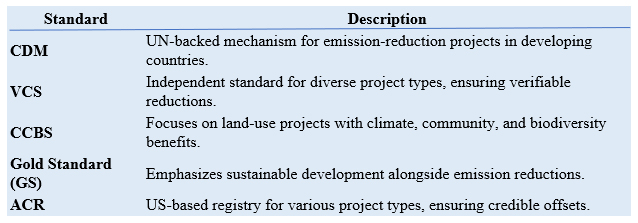
Carbon Credit Standards
Carbon credit standards provide protocols for creating, verifying, and trading credits. Key standards include:
Calculation Methodology
The general approach to calculate carbon credits involves three steps:
- Calculate Emission Reductions: Compare emissions from a baseline scenario (e.g., fossil fuel-based power) to the renewable energy project’s emissions (typically zero for solar).
- Apply Conversion Factor: Convert reductions into credits based on the standard’s rules (e.g., 1 credit = 1 tonne CO2e for VCS).
- Issue Credits: Credits are issued post-verification, reflecting verified reductions.
Case Study: 1 MW Solar Power Plant
Assumptions:
- Capacity: 1 MW
- Annual generation: 8,000 MWh
- Baseline emissions intensity: 500 g CO2e/kWh (grid or fossil fuel plant)
- Solar emissions intensity: 0 g CO2e/kWh
Clean Development Mechanism (CDM)
- Formula:
Emissions Reduction = (Capacity × Generation × Baseline Emissions Intensity) − (Capacity × Generation × Solar Emissions Intensity)
= (1 MW × 8,000 MWh × 500 g CO2e/kWh) − (1 MW × 8,000 MWh × 0 g CO2e/kWh)
= 4,000,000 kg CO2e = 4,000 tonnes CO2e - Emission Reduction Factor (ERF): 0.9 (90% of reductions recognized).
Credits = 4,000 tonnes × 0.9 = 3,600 credits. - Process: Verified by third-party auditors, approved by CDM Executive Board.
Verified Carbon Standard (VCS)
- Formula: Same as CDM.
Emissions Reduction = 4,000 tonnes CO2e. - Conversion Factor: 1 credit = 1 tonne CO2e.
Credits = 4,000 tonnes = 4,000 credits. - Process: Verified by VCS-approved auditors, credits issued directly.
CCBS, Gold Standard, and ACR
- Steps:
- Determine baseline emissions (e.g., 500 g CO2e/kWh).
- Calculate reductions (4,000 tonnes CO2e).
- Register and verify project with respective registry.
- Monitor performance to ensure accurate reductions.
- Issue credits based on verified reductions.
- Credits: Typically 4,000 credits (1:1 conversion), subject to standard-specific adjustments (e.g., GS may prioritize sustainable development criteria).
Comparison of Standards
Visualization: Carbon Credit Calculation Process
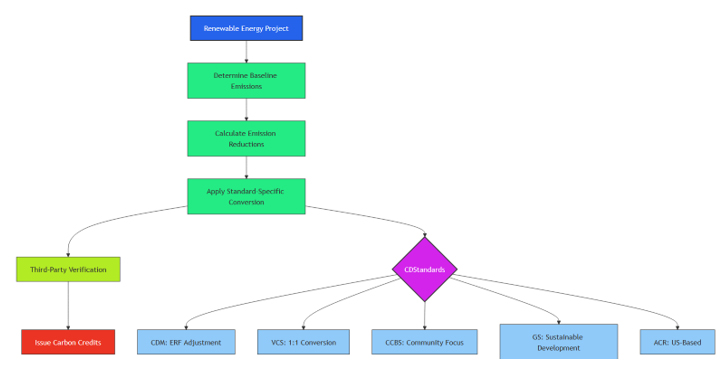
This diagram illustrates the workflow for calculating and issuing carbon credits, highlighting standard-specific variations.
