Hydrogen Fuel Cell Market: Trends, Revenue Models, and Future Outlook
The hydrogen fuel cell market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by global decarbonization efforts, technological advancements, and increasing demand for clean energy solutions. This write-up explores key market trends, revenue models, and the future outlook for the sector.
Market Trends
- Surging Demand for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
The transportation sector is a major driver, with hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) like the Toyota Mirai and Hyundai Nexo gaining traction. Passenger FCEVs are projected to hold a 78% market share in the near future, fueled by government subsidies such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act’s $7,500 tax credit per vehicle. In Asia-Pacific, China aims to produce 5,000 FCEVs for logistics and buses, while South Korea and Japan lead in passenger FCEV sales.
FCEV Market Share by Region
Region | Market Share (%) | Key Driver |
Asia-Pacific | 45% | Government initiatives (China, Japan) |
North America | 47% | Subsidies and R&D investments |
Europe | 37% by 2037 | Rapid infrastructure growth |
Sources: Web IDs 7, 11, 13, 19 |
- Expansion of Hydrogen Infrastructure
Governments and private sectors are investing heavily in hydrogen refueling networks. Japan plans for 320 refueling stations while California targets 100 stations to support 1.5 million zero-emission vehicles. This infrastructure growth is critical for scaling FCEV adoption, particularly in urban areas.
- Stationary Applications Gain Momentum
Stationary fuel cells for power generation in commercial, industrial, and residential sectors are growing, expected to hold a 45.1% market share in the coming years. They offer high efficiency (up to 60% vs. 35% for traditional plants), making them ideal for data centers and critical infrastructure like telecom towers.
- Technological Advancements in Fuel Cells
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) dominate with a 45.6% market share in 2024, prized for their efficiency and low-temperature operation, ideal for transportation. Innovations in materials and designs are reducing costs and improving durability, with companies like Ballard Power Systems and Hyundai leading R&D efforts.
Revenue Models
The hydrogen fuel cell market employs diverse revenue models to capitalize on its applications across sectors:
- Product Sales and Licensing
Companies like Toyota and Ballard Power Systems generate revenue by selling fuel cell stacks and licensing technology to OEMs. For instance, Toyota plans to produce 10,000 Mirai vehicles annually while Ballard supplies systems for projects like the Hollandse Kust Noord wind project. - Service and Maintenance Contracts
Providers offer long-term maintenance contracts for stationary fuel cells, ensuring reliability for applications like data centers. This model ensures recurring revenue, especially for large-scale installations. - Infrastructure Development Partnerships
Governments and private firms collaborate on refueling infrastructure, with revenue shared through public-private partnerships (PPPs). For example, 82 MOBILITY raised $135 million in 2022 to expand H2 stations with Shell and Air Liquide. - Subscription and Leasing Models
Emerging models include leasing fuel cell systems for commercial fleets or offering hydrogen-as-a-service (HaaS), where users pay per kilogram of hydrogen used, reducing upfront costs for adopters.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Revenue Models

Future Outlook (2025–2037)
The hydrogen fuel cell market is poised for significant growth, with varying projections reflecting optimism:
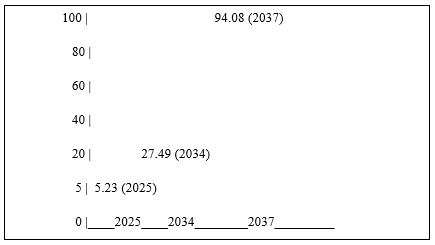
- Market Size Growth: The market, currently valued at $5.23 billion, is expected to reach $27.49 billion by 2034 (CAGR 20.24%), with some estimates as high as $94.08 billion by 2037 (CAGR 23.3%). The FCEV market alone may hit $16.79 billion by 2030 (CAGR 47.5%).
- Regional Leadership: North America will likely maintain dominance with a 50% share by 2037, driven by U.S. R&D investments like the DOE’s $750 million program. Asia-Pacific, however, is the fastest-growing region, with China and South Korea scaling production and infrastructure.
- Emerging Applications: Beyond transportation, hydrogen fuel cells will expand into aviation (e.g., synthetic kerosene), maritime (e.g., fuel cell ships), and industrial heating, displacing natural gas. By 2040, mobility applications could account for 80 Mtpa of clean hydrogen demand in optimistic scenarios.
- Challenges and Opportunities: High production costs, hydrogen storage limitations, and refueling times remain hurdles. However, advancements in electrolysis for clean hydrogen production and supportive policies (e.g., EU’s 50% carbon reduction target by 2030 for chemicals) will drive adoption.
Conclusion
The hydrogen fuel cell market is at a pivotal stage, with transportation and stationary applications leading growth. Diverse revenue models, from product sales to infrastructure partnerships, are enabling scalability, while future projections highlight a robust trajectory toward a clean energy future. However, overcoming cost and infrastructure barriers will be key to realizing this potential, particularly as global decarbonization efforts intensify.
